Mastering IT Risks: An In-Depth English Analysis
This document provides a comprehensive English perspective on navigating information technolo risks. It explores various aspects of IT risks, offering strategies and solutions for mitigating them. The text emphasizes the importance of understanding risks, implementing effective security measures, and maintaining continuous vigilance in the r-evolving IT landscape.
[Image: A visual representation of the digital landscape, illustrating the interconnectedness of technolo in various aspects of life.]
1. Cybersecurity Threats
Cybersecurity threats are among the most siificant risks in the realm of information technolo. As cybercriminals become increasingly sophisticated, the threat landscape continues to broaden. Common cybersecurity risks include:
Phishing Attacks: Cybercriminals send fraudulent emails that mimic reputable sources, duping users into raling sensitive information.
Malware: Software desied to harm, disrupt, or gain unauthorized access to comr systems.
Ransomware: A form of malware that encrypts files on a victim's comr, demanding a ransom for the restoration of access.
To mitigate these risks, organizations and individuals should:
Implement Strong Security Measures: Utilize firewalls, antivirus software, and robust passwords.
Educate Employees and Users: Regularly train employees and users to recoize and respond to cybersecurity threats.
Backup Data: Regularly backup critical data to prnt data loss in the nt of a cyber attack.
2. Data Breaches
Data breaches represent another siificant risk within the IT domain. Such breaches can result in substantial financial and reputational damage. Common causes of data breaches include:
Insider Threats: Employees or contractors with authorized access to sensitive data misuse their privileges.
Physical Security Breaches: Theft or loss of physical devices containing sensitive information.
Software Vulnerabilities: Exploitable weaknesses in software that can be exploited by cybercriminals.
To prnt data breaches, organizations should:
Conduct Regular Security Audits: Identify and rectify vulnerabilities in IT systems.
Implement Access Controls: Limit access to sensitive data to only those who require it.
Train Employees on Data Security: Ensure that employees are coizant of the importance of data protection.
3. Technological Obsolescence
The rapid pace of technological innovation means that IT systems can quickly become outdated. This poses risks of decreased efficiency, increased costs, and a competitive disadvantage. To ma this risk, organizations should:
Stay Informed: Keep abreast of the latest technological advancements and industry trends.
Plan for System Upgrades: Regularly assess the need for upgrading IT systems to ensure they remain effective and secure.
Invest in Training: Provide training for employees to adapt to new technologies and workflows.
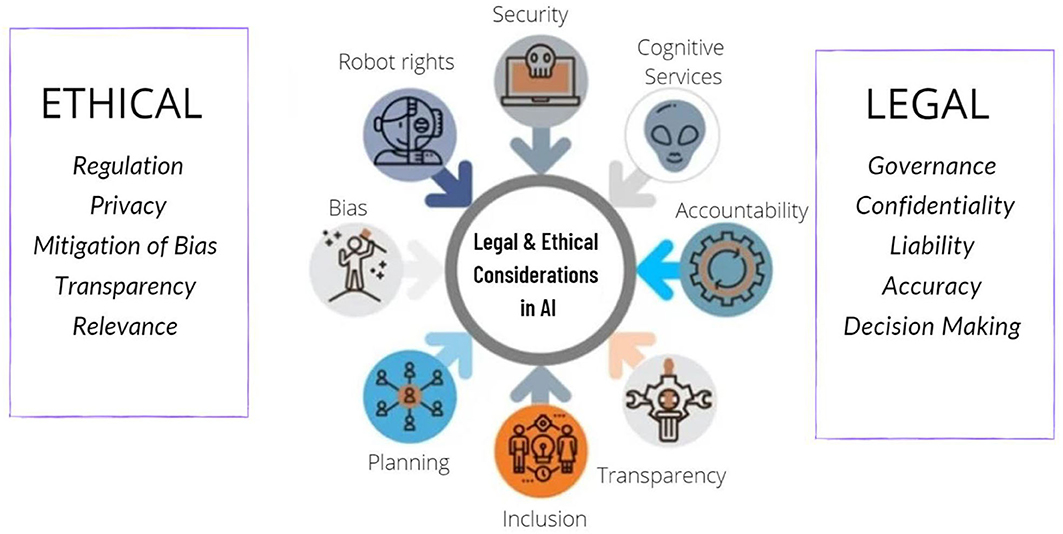
4. Privacy Concerns
With the growing volume of personal data collected and stored by organizations, privacy concerns have become a siificant issue. Data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, impose stringent requirements on the handling of personal data. To address privacy concerns, organizations should:
Comply with Data Protection Regulations: Ensure that all data handling practices are in line with applicable laws and regulations.
Implement Privacy by Desi: Integrate privacy considerations into the desi of IT systems and processes.
Provide Transparency: Clearly communicate how personal data is collected, used, and protected.
5. Digital Divide
The digital divide refers to the gap between those who have access to digital technolo and those who do not. This gap can lead to disparities in education, employment, and social inclusion. To address the digital divide, efforts should be made to:
Expand Internet Access: Increase the availability of affordable internet services in underserved areas.
Provide Digital Literacy Training: Educate individuals on how to use digital technolo effectively.
Support Inclusive Policies: Advocate for policies that promote digital equality and accessibility.
In conclusion, information technolo risks are a complex and multifaceted issue. By comprehending the various risks and implementing appropriate mitigation strategies, organizations and individuals can navigate the digital landscape more safely and securely. As technolo continues to evolve, it is imperative to remain vigilant and proactive in managing these risks to ensure a sustainable and inclusive future.
我要评论